Table of Contents
Hybrid Electric Vehicles Basics
1. Overview
Hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs) are actually powered by an internal combustion engine and an electric propulsion system which uses electrical energy stored in a small battery pack. A hybrid electric vehicle cannot be plugged into an EV charger like plug-in hybrid vehicles and battery electric vehicles. Instead the battery is charged through a mechanism called regenerative braking and by the internal combustion engine. HEVs combine the benefits of high fuel economy and low tailpipe emissions with the range of a normal and conventional car. In a HEV the mechanical power is delivered sometimes by the electric motor, sometimes by the gas engine and sometimes by both at the same time. A wide range of hybrid electric vehicles are currently available in the market and often more expensive than similar conventional vehicles but some cost may be recovered through fuel saving and state incentives.
2. What are the key components of a Hybrid Electric Vehicle?
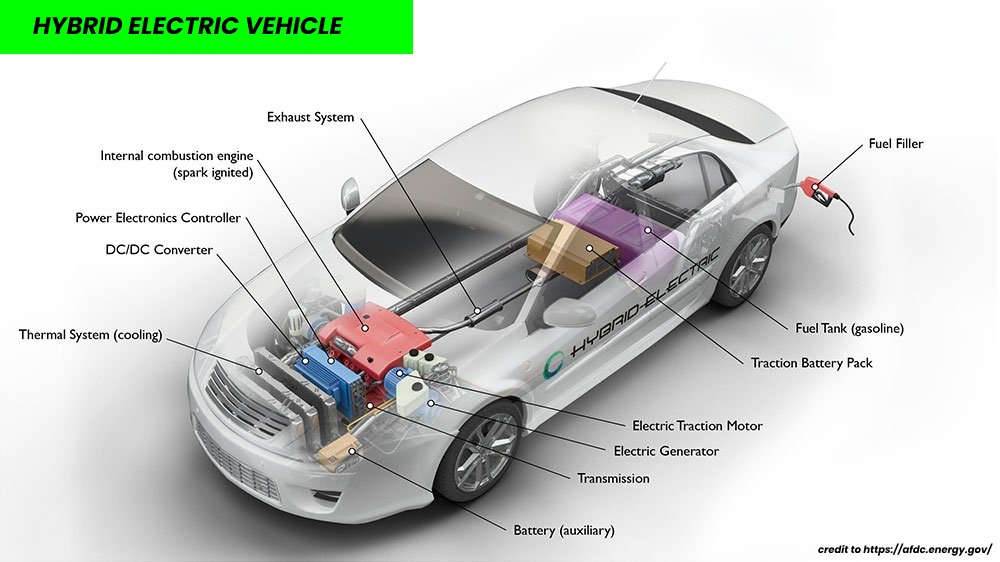
The key components of a Hybrid Electric Vehicle are :
- Electric traction motor : By pulling energy from the battery pack, the electric motor drives the vehicle’s wheels. Some cars use motor generators that perform both functions, driving the car and electricity generation.
- Electric generator : Hybrid electric vehicles can generate electricity from wheels while braking. This functionality is called regenerative braking and in some cars is done using a stand alone electric generator but in some HEVs it is done using motor generators.
- DC/DC Converter : This device converts DC high-voltage coming from the battery pack to DC low-voltage in order to feed the vehicle accessories and recharge the auxiliary battery.
- Traction Battery pack : This battery pack consists of rechargeable lithium-ion cells that are charged during regenerative braking or by the internal combustion engine, it stores electricity for use by the electric traction motor.
- Power electronics controller : This unit manages the flow of electricity delivered by the traction battery pack to the electric motor controlling the speed and the torque produced.
- Auxiliary battery : The role of this battery is it provides electricity to start the car before the traction battery pack is engaged and it also powers vehicle accessories.
- Internal combustion engine : Like any conventional car, in the internal combustion engine the fuel is injected into the intake manifold or the combustion chamber, where it is combined with air, and the air/fuel mixture is ignited by the spark from a spark plug.
- Fuel tank : This unit stores the fuel on board the vehicle until it is needed by the engine.
- Fuel filler : A fuel filler is the opening through which fuel (gasoline or diesel) is added to a vehicle’s fuel tank. This opening is generally located on the exterior of the vehicle and often on the back of the car. It is covered by a fuel filler cap to protect the fuel system from dust, debris, and unauthorized elements.
- Exhaust system : The role of exhaust system is to channel exhaust gases coming from the engine out through the tailpipe. HEVs are equipped with a three-way catalyst designed to reduce engine-out emissions within the exhaust system.
- Transmission : The transmission transfers mechanical power from the engine and/or electric traction motor to drive the wheels.
- Thermal management system : This unit usually consists of a radiator, fan and a coolant pump and it helps to maintain a proper operating temperature range of the engine, battery pack, electric motor, power electronics and other components.
3. Types of Hybrid Electric Vehicles?
Most people have heard of Hybrid electric vehicles, but few of them are actually aware of the various types that exist out there on the market. HEVs can either be mild or full hybrids.
Mild hybrids : Also called micro hybrids are one of the newest innovations in hybrid technology; they use a battery and an electric motor to help power the vehicle when accelerating from a dead stop and assist the engine to shut off when the vehicle is stopping. A mild hybrid system cannot power the vehicle using electricity alone like a full hybrid car. These vehicles cost less than full hybrids but provide less fuel economy.
Full Hybrids : Full Hybrids have larger batteries and more powerful electric motors, which can drive the car for short distances at low speed unlike mild hybrids. And when it comes to full hybrid vehicles we can distinguish three types of powertrains configurations :
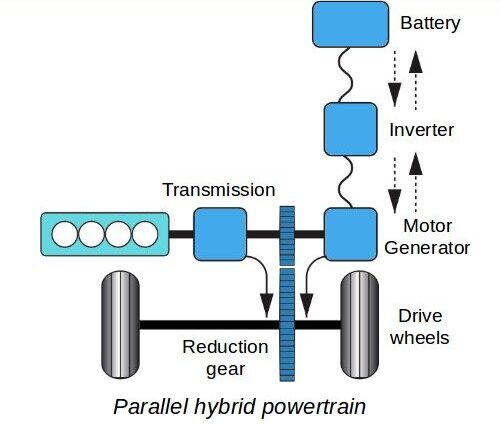
- Parallel Hybrids : with parallel hybrids the wheels can be powered in one of 3 ways, either directly by the internal combustion engine or directly by the electric motor or by both systems at same time.
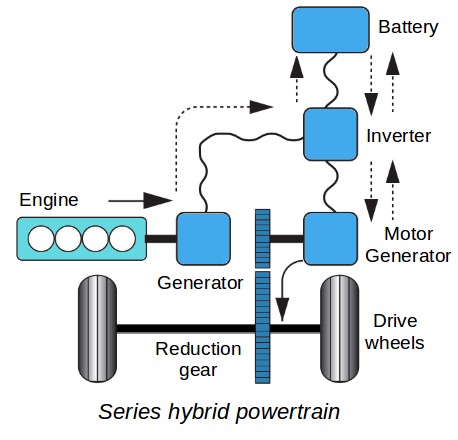
- Series Hybrids : In series hybrids the wheels are powered only by the electric motor. With the internal combustion engine providing power to the electric generator which then sends the electrical power to the electric motor and/or the battery pack.
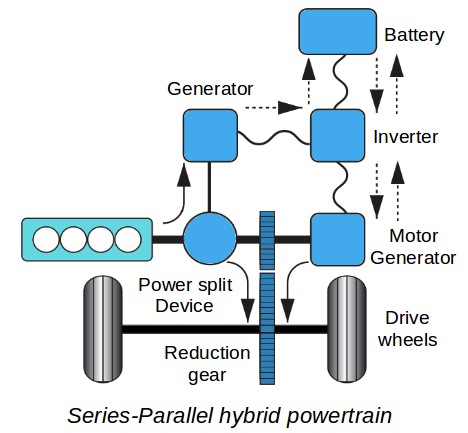
- Series-parallel hybrids : With a mechanical power split a series-parallel hybrid combines the features of both, series and parallel hybrids, to offer the best of both, with the on-board computer system choosing the most efficient way to operate at any given time.
4. Advantages and Disadvantages of Hybrid Electric Vehicles?
Hybrid Electric Vehicles have been on the market for quite a while now. And like any car there are certain benefits and drawbacks of using a hybrid electric car and here are the top few to keep in mind :
Advantages :
- Hybrid vehicles are fuel efficient, in fact when compared to traditional petrol/gasoline powered vehicles they can achieve significantly better efficiency, thus cost saving over time particularly for those who drive most of their time in cites.
- Hybrid vehicles emit less greenhouse gasses than conventional cars which can help reduce air pollution and improve overall air quality.
- Hybrid vehicles require less maintenance than conventional cars.
Disadvantages :
- Hybrid vehicles tend to cost more than traditional vehicles.
- Hybrid vehicles are complex to maintain, they require more specialized maintenance than traditional cars.
- Hybrid cars usually have a higher insurance cost than petrol/diesel cars because the technology used inside them is much more expensive to repair or replace.
- Hybrid vehicles’ batteries can also cost more to replace than a standard car battery (BEV). However, you shouldn’t need to replace these too often, as most manufacturers generally offer five years, or 100,000 km warranty on them.
















