Table of Contents
Fuel Cell Electric Vehicles Basics
1. Overview
Fuel Cell Electric vehicles (FCEVs) are quite similar in operation to the battery electric vehicles except that FCEVs are powered by hydrogen, the most abundant element in the universe. The biggest difference between a BEV and a FCEV is that in a BEV the power is stored in a battery traction pack than delivered to the electric motor, instead in a FCEV the power is generated by taking compressed hydrogen from the vehicle’s tank and mixing it with the atmospheric air inside an onboard fuel cell stack to produce DC electricity, this electricity then powers the electric traction motor. Unlike conventional internal combustion engine vehicles, these vehicles produce no harmful tailpipe emissions, the only by-product produced by a FCEV is water which exhausts through the tailpipe. FCEVs are generally equipped with other advanced technologies in order to increase efficiency, such as regenerative braking systems that capture the energy usually lost during braking and store it in a battery.
2. What are the key components of a Fuel cell Electric Vehicle?
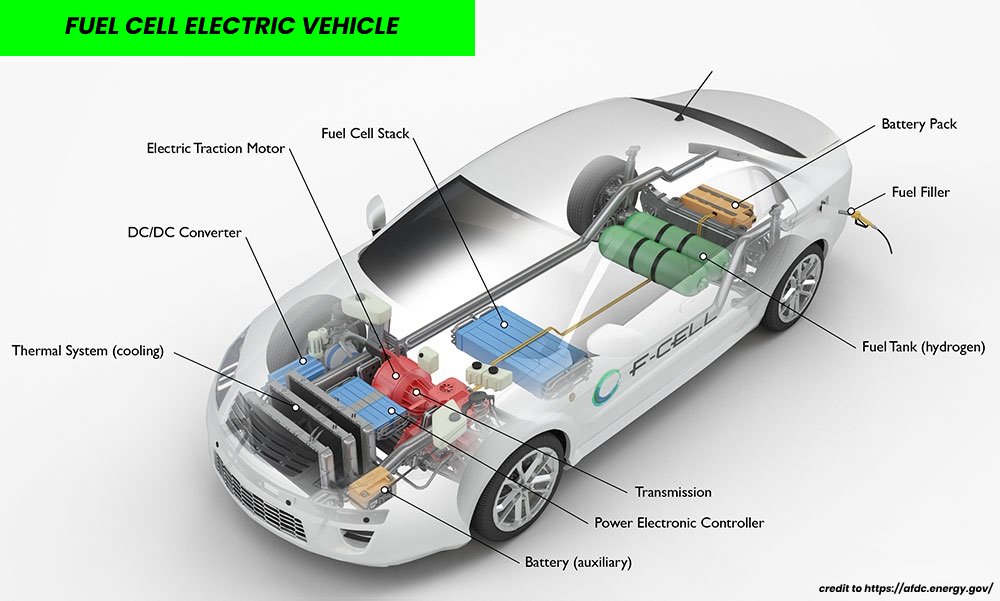
The key components of a Fuel Cell Electric Vehicle are :
- Fuel cell stack : The fuel cell stack is the core of a fuel cell electric vehicle it is this unit that produces electricity from hydrogen mixed with atmospheric air, The fuel cell stack is a highly efficient and environmentally-friendly way to produce electric power, making FCEVs one of the cleanest EV out there on the market.
- Electric traction motor : The electric traction motor is the primary source of propulsion in an FCEV it gets energy from both the fuel cell stack and the battery pack, the electric motor drives the vehicle’s wheels and it is normally located in close proximity to the wheels. Some FCEVs use motor generators that perform two functions, driving the car and electricity generation during braking.
- DC/DC Converter : This device converts DC high-voltage coming from the battery pack to DC low-voltage in order to feed the vehicle accessories and recharge the auxiliary battery.
- Battery pack : This battery pack is used to store excess energy produced by the fuel cell stack and/or during regenerative braking, it consists typically of rechargeable lithium-ion cells interconnected to create a high-capacity storage system.
- Power electronics controller : This unit manages the flow of electricity between the fuel cell stack, the battery pack and the electric traction motor controlling the speed and the torque produced. It helps the car to operate at maximum efficiency and performance.
- Auxiliary battery : The role of this battery is it provides electricity to start the car and power vehicle’s accessories before the fuel cell stack is totally engaged and producing enough electricity.
- Fuel tank : This unit stores hydrogen on board the vehicle until it is needed, it is usually made of lightweight materials such as carbon fiber, and designed in a way to stand the high pressure of the hydrogen fuel.
- Fuel filler : A fuel filler is the opening through which hydrogen fuel is added to the vehicle’s fuel tank. This opening is generally located on the exterior of the vehicle and often on the back of the car. It is covered by a fuel filler cap to protect the fuel system from dust, debris, and unauthorized elements and to ensure the safe and efficient transfer of hydrogen fuel.
- Exhaust system : The primary function of the exhaust system is to efficiently channel out water vapor generated by the fuel cell stack through the tailpipe.
- Transmission : The transmission transfers mechanical power from the electric traction motor to the wheels. It is designed to allow the motor to operate at efficient speeds and optimal torque.
- Thermal management system : This unit usually consists of a radiator, fan and a coolant pump and it helps to regulate and maintain a proper operating temperature range for the fuel cell stack, battery pack, electric motor, power electronics and other components.
3. How far will a fuel cell electric vehicle can go when it is fully charged?
Fuel cell electric vehicles can carry in their tanks enough hydrogen for around 300 to 400 miles of range, and they can be refueled with hydrogen the same way conventional petrol or diesel cars do. In fact filling up takes between 3-5 minutes for a full tank.
4. Why are fuel cell electric vehicles expensive?

Fuel cell hydrogen cars models that exist already on the market generally cost more than the other types of electric vehicles (BEV, PHEV, HEV, RE-EV). The reasons why FCEVs are currently more expensive are :
- Production lines are not yet fully developed which means that assembly lines for hydrogen fuel cell cars are not optimized and efficient as those of conventional cars.
- Low production volumes is also a factor, and higher production volumes are expected to lower the overall costs.
- Platinum is a key component in fuel cell systems, serving as a catalyst in the electrochemical reactions that produce electricity. The demand for platinum is significantly impacting the overall cost of fuel cell electric vehicles.
5. Why is the cost of hydrogen fuel so expensive?
One of the primary reasons why the cost of hydrogen fuel is higher than gasoline and diesel is the current poor charging infrastructure, along with the high costs associated with transportation and storage. Furthermore, the production of hydrogen fuel requires significant investment in both energy and equipment. But if the production of hydrogen increases worldwide the price will certainly decrease.
6. Advantages and Disadvantages of Fuel Cell Electric Vehicles?
Fuel cell Electric Vehicles are among the most exciting developments in the electric mobility era. But like any other vehicle there are certain benefits and drawbacks of using a fuel cell electric vehicle and here are the top few to keep in mind :
Advantages :
- Fuel cell electric vehicles are more efficient than conventional vehicles. And similar to electric vehicles and hybrid electric vehicles, these vehicles are capable of capturing the energy lost during braking and storing it in the battery.
- Fuel cell electric vehicles produce zero carbon emissions, only water vapor and warm air are exhausted.
- Unlike battery electric vehicles that have been criticized for their long recharging time, fuel cell electric vehicles can be refueled in a matter of minutes like conventional cars.
Disadvantages :
- Fuel cell electric vehicles are expensive.
- Refueling stations are limited and a heavy investment should be done in order to build a compiling infrastructure.
- Refueling cost is significantly more than the cost of charging an electric car or filling up a combustion engine.
















