Table of Contents
Electric Bikes Basics
1. Overview
Electric bikes technology has gained popularity and advanced in recent years, there are more and more of them on our streets, since they offer many benefits and advantages. Actually an electric bike is just a regular bicycle with the addition of an electric motor, a rechargeable battery, and a controller, in order to assist the rider.
2. What are the key components of an Electric Bike?
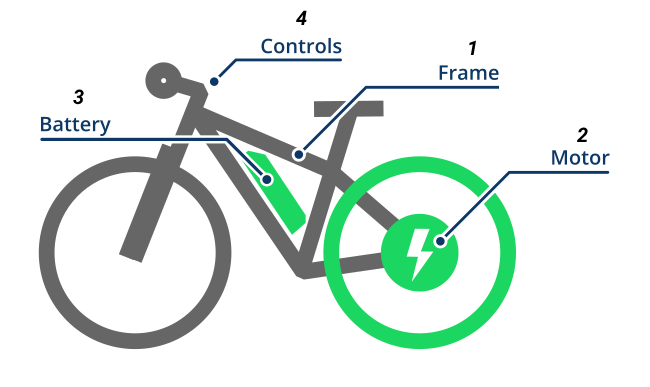
The main key components of an electric bike are :
- Frame : Similar to conventional bicycles, electric bikes also come with a foundational bike frame. Typically the design of e-bike frames differs slightly from non-electric bikes in order to optimize the placement of the battery and motor.
- Motor : The electric bike’s motor is the unit providing the additional boost of assistance to the rider. Similar to a car engine, certain e-bike motors can vary in terms of power, weight, and efficiency. While many brands offer e-bike motors, the majority of electric bikes feature one of two common motor styles :
Mid-drive : Mid-drive motors are housed in the middle of the bike, at the center of where you pedal. They come in a range of different power capacities and provide a stable center of gravity and smooth support that feels more natural when pedaling.
hub-drive : Hub-drive motors are housed inside the hub of the rear wheel, near the bicycle’s back gears (like in the picture above). They are generally more affordable and lightweight than mid-drive motors, which make it easier to find one that fits your budget, so all you have to do is hop on and go - Battery : E-bike battery represents the unit that powers the motor by providing electrical energy stored on it. However, batteries vary greatly in size, shape, location, and wattage. How many watt-hours a battery holds directly impacts how fast and how far you can go assisted.
- Controls : E-bikes usually house many essential controls on its handlebar that will give you full control over your e-bike , such as the brake lever, display screen, and controllers. And when it comes to controllers there’s generally two main types of controllers, throttle and pedal assist. Throttle e-bikes use a throttle on the handlebars to engage the electric motor when twisted or pressed. You don’t even need to pedal, although the less you pedal the sooner your battery will run out of power. Pedal assist e-bikes or pedelecs engage the motor only when you pedal, and provide different levels of assistance. Some e-bikes come with both throttle and pedal-assist so you can use both options.
3. What do Class 1,2 and 3 bikes mean?
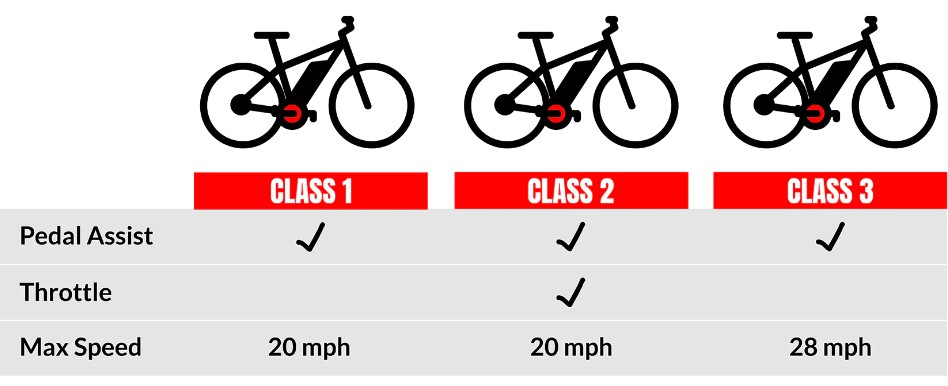
If you’re new to the world of electric bikes, probably you may have heard terms like Class 1, Class 2, and Class 3. So let’s break down the differences between these classes :
- Class 1 e-bikes are limited to a top speed of 20 miles per hour, and the electric motor works only when the rider is pedaling which means you must pedal to use the electric motor. It is just like riding a conventional bicycle but with the added benefit of a motor that senses your pedaling. Note that when an e-bike has an electric motor that assists only during pedaling it is called a pedelec.
- Class 2 e-bikes are also like class 1 e-bikes; they are limited to top speed of 20 miles per hour, but they are equipped with throttle that allow you to benefit from the motor without having to peda, simply press the throttle, and go. This feature allows you to accelerate rapidly without the need to pedal but the more you rely on the throttle without pedaling, the quicker you will drain the battery.
- Class 3 e-bikes are the fastest legal electric bikes out there, they can go up to 28 miles per hour and are equipped with a speedometer, they may and may not have a throttle but in most cases they provide only pedal assistance just like class 1. Class 3 e-bikes are still considered bicycles and do not require a driver’s license.
4. What are the different types of e-bikes?
Ebikes are available in a variety of styles, designed for different purposes. Each style is tailored to a particular terrain and type of ride. Here are a few examples of the most common categories :
- Comfort/Cruiser : Cruiser e-bikes are best suited for recreational riders that want comfort and control as they cruise. When you have an e-bike of this type you will sit upright and have a super comfy saddle. They are designed mostly for flat terrains like bike paths and paved roads. They have wide tires and usually come with a suspension system to reduce shocks.
- Hybrid/Commuter : A commuter e-bike is generally good for running errands, commuting to work or getting where you want to go fast. These types of e-bikes are designed to go far and fast, they typically have the longest range and can go as fast as 28 miles per hour. Many e-bikes of this category are equipped with a rack to carry objects, convenient for transporting items such as your laptop, groceries, or additional stuff.
- Mountain/Off-road : Most of the mountain e-bikes will be Class 1 only, they are built specifically for thrill-seekers who want to venture into off roading trails but if you live on the mountain it is a good option for you. They come generally with wide tires and flat handlebars to help riders tackle rugged terrain and dirt trails.
5. Advantages and Disadvantages of an Electric bike?
Electric bikes are getting people’s attention more and more. And like any technology there are certain benefits and downsides of using an electric bike and here are some to keep in mind :
Advantages :
- Electric bikes are eco-friendly compared to other means of transportation, they are great for both short and long commutes.
- Electric bikes compared to traditional bikes are easy to get started with, unlike traditional bikes that rely solely on muscle power, e-bikes on the contrary are assisted by the electric motor which lower the barrier to entry into the cycling lifestyle.
- When compared to the other means of transportation e-bikes are clearly one of the cheapest ways to get around.
- Using an electric bike as a regular way to get around is a great way to introduce some physical activity to your everyday routine, thus improving your overall health.
- For many folks, electric bikes make it possible to enjoy more time with friends and family members allowing them to join together on recreational bike rides.
Disadvantages :
- Electric bikes generally cost more to buy and to maintain than traditional bikes, in fact the first time people learn about an e-bike they get surprised by the cost which typically ranges anywhere from $1000 to $10.000.
- One of the disadvantages compared to traditional bikes is that e-bikes are heavier. Since they have additional components like the electric motor and the battery which make them bulky and unwieldy in situations where you need to pedal without electric assistance.
- Electric bikes are still relatively new, which make regulations confusing, e-bikes classifications tend to vary across states and countries. As a result, trying to figure out the rules for riding your e-bike can be perplexing.
















