Table of Contents
Battery Electric Vehicles Basics
1. Overview
A battery Electric Vehicle (BEV), pure electric vehicle, fully electric vehicle or simply all-electric vehicle is a type of electric car that uses only electrical energy stored in rechargeable battery packs to power the car instead of burning petrol or diesel and with no secondary source of propulsion. BEVs use electric motors instead of internal combustion engines for propulsion. They pull all the power from a giant battery pack which is actually a pack of thousands of individual rechargeable lithium-ion cells. And Because it runs only on electric, the vehicle emits no exhaust from a tailpipe and does not contain the typical liquid fuel components, such as a fuel pump, fuel line, or fuel tank.
(Check out our article on: Top 10 EVs in 2023)
2. What are the key components of a Battery Electric Vehicle?
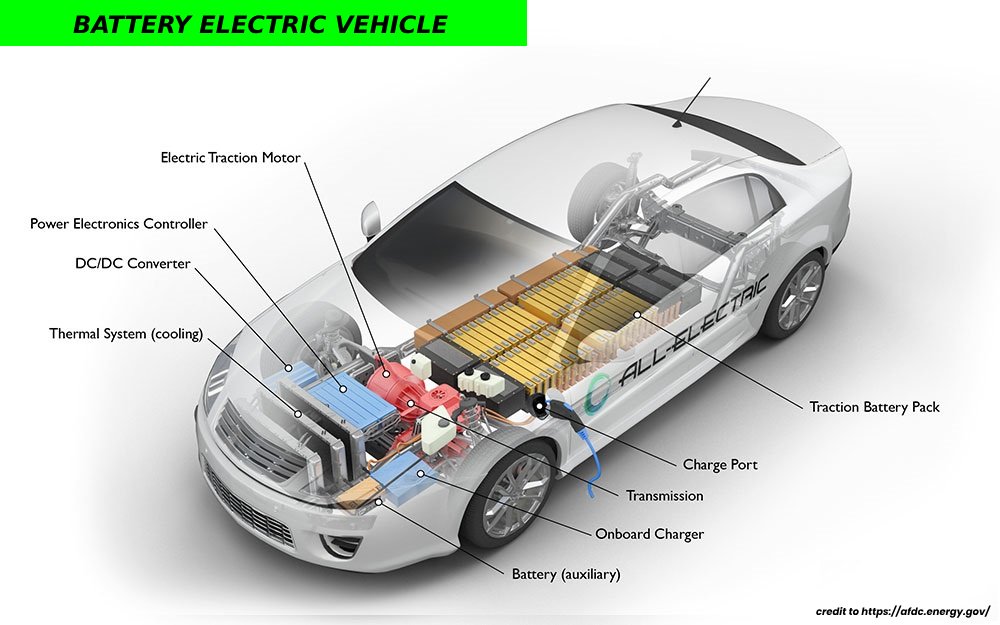
The key components of a Battery Electric Vehicle are :
- Traction Battery pack : The battery pack, consisting of thousands of rechargeable lithium-ion cells is the most important and expensive component of a battery electric vehicle . The battery acts as an electrical storage system and the higher the kW of a battery is the more miles the car will travel.
- Onboard charger : The onboard charger is used to convert AC current coming from a level 1 or level 2 EV charger to DC current and then store it in the battery. The onboard charger is located inside the vehicle.
- Power electronics controller : This equipment is the one responsible for regulating the electrical energy coming from the battery pack to the electrical motor controlling the speed of the electric traction motor and torque it produces.
- DC/DC Converter : The DC/DC Converter is an equipment that converts power coming from the battery pack from DC high voltage to DC low voltage needed to run vehicle accessories and recharge the auxiliary battery.
- Charge port: The charge port allows the vehicle to be connected to an external power supply in order to charge the battery pack.
Electric traction motor : Battery Electric Vehicles use an electric motor or two to drive the wheels. The electrical energy comes from the battery pack via the controller. - Auxiliary battery : In absence of the main battery (battery pack) the auxiliary battery will continue to provide energy to the accessories in the electric vehicle, and it prevents the voltage drop produced during engine start.
- Transmission : The mechanical power coming from the electric motor is transferred to the wheels via the transmission system and because the electric cars don’t require multi-speed transmission the efficiency of the transmission is very high.
- Thermal management system : This unit usually consists of a radiator, fan and a coolant pump and it helps to maintain a proper operating temperature range of the battery pack, electric motor, and power electronics inside the car.
3. How far will a battery electric vehicle go when the battery is fully charged?

How far you can get in an electric car when the battery is fully charged is an important question for many people when thinking of buying a new car but there is no single correct answer to this question. Each BEV will have its own published figures based on standard tests, but generally, the more kilowatts the battery holds, the longer the driving range and the further the car can travel on single charge. But to give you an idea about the range of an electric car we will give you some samples of BEVs existing right now on the market with the range of each one of them :
- Lucid Air Dream Edition : 685 km (426 miles)
- Tesla Model Y : 455 km (283 miles)
- Mini Cooper 3 : 160 km (100 miles)
- Fiat 500e Hatchback 24 kwh : 135 km (84 miles)
However, many things in daily driving can affect how long a charge will last, including cold weather, how fast a car is driven, how often the AC or the heater is turned on. All of which can drain the battery faster. Check out our article on: Five Tips To Save As Much Range As Possible During Winter.
4. What happens when a BEV runs out of charge?
What happens when a Battery Electric Vehicles runs out of charge is a good question but in reality what you should ask is how can i avoid that my BEV runs out of battery as you would pay attention to gas gauge in a conventional car you will have to do the same in a BEV. As long as you pay attention to your car’s battery charge indicator, you should not be worried about running out of battery. And most vehicles come with a GPS and will provide you with a map to the nearest charging station’s location. Check out our article on: EV Charging Basics.

5. Advantages and Disadvantages of Battery Electric Vehicles?
Battery Electric Vehicles are now growing in popularity every day. And like conventional cars there are certain benefits and drawbacks of using an electric car and here are the top few to keep in mind :
Advantages :
- Battery Electric cars are energy efficient, it is around 3 times more efficient than gas-powered cars.
- Battery Electric cars reduce emissions because they rely on rechargeable batteries.
- Battery Electric cars actually perform better and don’t need much maintenance like other cars.
- Better driving experience.
- Federal tax credit.
Disadvantages :
- Battery Electric Vehicles can be expensive, in fact usually BEVs have a higher price compared to conventional cars but you can save money over time since there is generally less maintenance federal tax credit.
- Battery Electric Vehicles take a long time to recharge, for example full charging a battery pack with level 1 or level 2 charger can take around 8 hours but with DC fast charging it can take around 30 minutes to recharge.
- Traveling distance, in fact one of the big concerns for any potential BEV owner is how far the car can drive. Early models had less than 100 miles but nowadays the modern BEVs can easily exceed 200 or even 300 miles.
















